‘Oppenheimer’ stirs up conflicted history for Los Alamos and New Mexico downwinders
The Hindu
An outreach co-ordinator with Union of Concerned scientists said, in developing nuclear weapons, the U.S. government effectively “poisoned its own people, many of whom are still waiting for recognition and justice”
The movie about a man who changed the course of the world’s history by shepherding the development of the first atomic bomb is expected to be a blockbuster, dramatic and full of suspense.
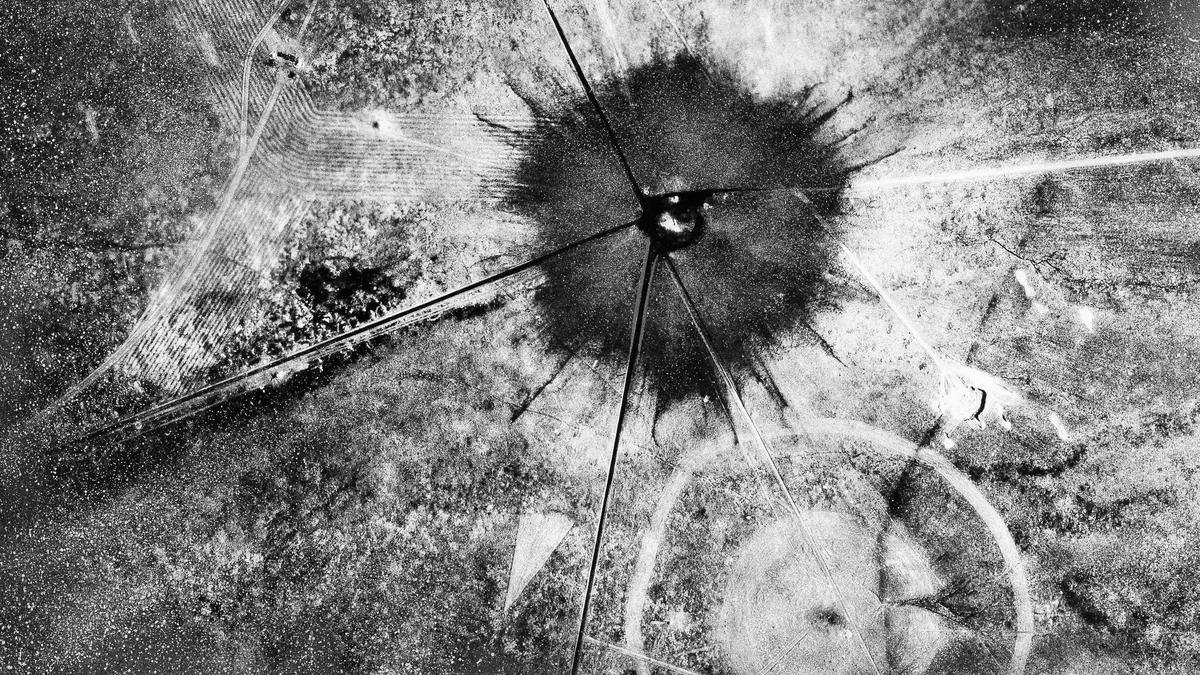
On the sidelines will be a community downwind from the testing site in the southern New Mexico desert, the impacts of which the U.S. government never has fully acknowledged. The movie on the life of scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer and the top-secret work of the Manhattan Project sheds no light on those residents’ pain.
“They’ll never reflect on the fact that New Mexicans gave their lives. They did the dirtiest of jobs. They invaded our lives and our lands and then they left,” Tina Cordova, a cancer survivor and founder of a group of New Mexico downwinders, said of the scientists and military officials who established a secret city in Los Alamos during the 1940s and tested their work at the Trinity Site some 200 miles (322 kilometers) away.
Cordova’s group, the Tularosa Basin Downwinders Consortium, has been working with the Union of Concerned Scientists and others for years to bring attention to what the Manhattan Project did to people in New Mexico.
While film critics celebrate Oppenheimer and officials in Los Alamos prepare for the spotlight to be on their town, downwinders remain frustrated with the U.S. government — and now movie producers — for not recognizing their plight.
Advocates held vigils Saturday on the 78th anniversary of the Trinity Test in New Mexico and in New York City, where director Christopher Nolan and others participated in a panel discussion following a special screening of the film.
Nolan has called the Trinity Test an extraordinary moment in human history.













