Upper stage of historic PSLV-37 mission re-enters Earth’s atmosphere eight years after launch: ISRO
The Hindu
The atmospheric re-entry of the rocket body within eight years of its launch is fully compliant with the international debris mitigation guidelines, in particular, the guideline of Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) that recommends limiting the post-mission orbital life of a defunct object in Low-Earth orbit (LEO) to 25 years.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) informed that the upper stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C-37 (PSLV C-37 mission) re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere on October 6.
The PSLV-C37 mission was launched on February 15, 2017 with Cartosat-2D as the main payload along with another 103 satellites as co-passengers, namely INS-1A, INS- 1B, Al-Farabi 1, BGUSAT, DIDO-2, Nayif 1, PEASS, 88 Flock-3p satellites, and 8 Lemur-2 satellites. The space agency created history as it was the first mission to launch 104 satellites with a single vehicle.
After injecting the satellites and passivation, the upper stage (PS4) was left at an orbit of approximately 470x494 km.
“It was regularly tracked by US Space Command (USSPACECOM) as an object with NORAD id 42052. Its orbital altitude slowly decayed, primarily due to atmospheric drag effects,” ISRO informed on October 8.
Since September 2024, ISRO System for Safe and Sustainable Space Operations Management (IS4OM) regularly monitored the orbital decay as part of its regular activities and predicted re-entry into the atmosphere in the first week of October 2024.
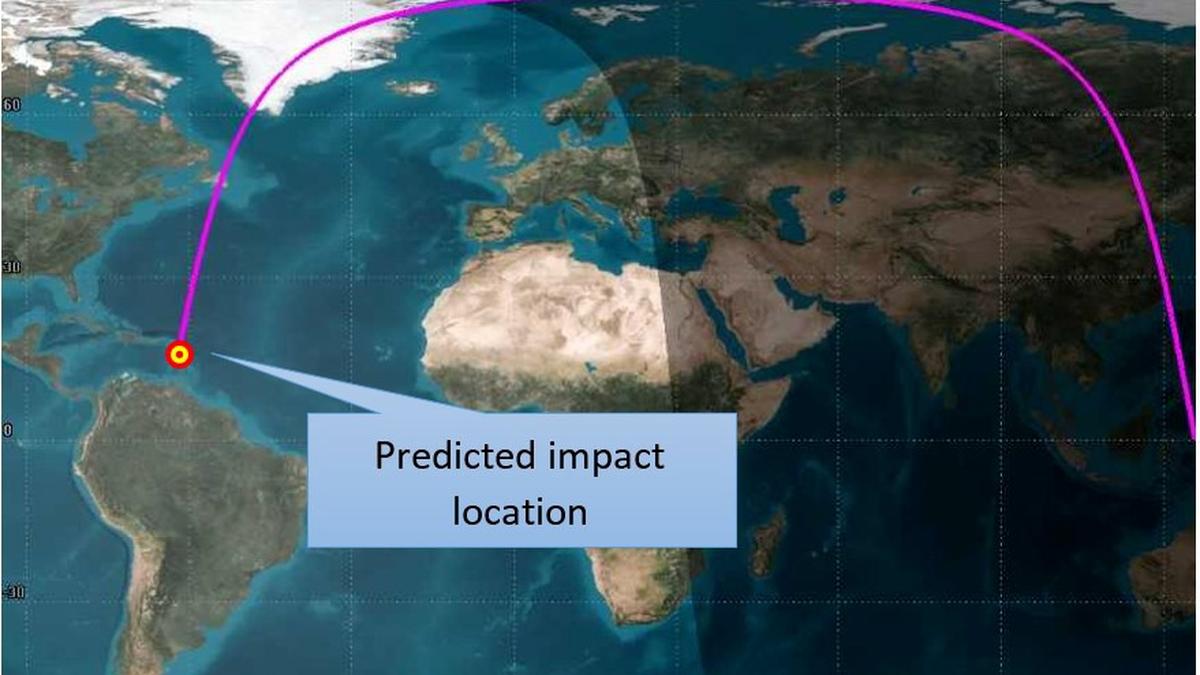
“The orbit had decayed to a size of 134x148 km, as of October 6, 2024 12:45 UTC. As per USSPACECOM prediction published in Space Track, the re-entry took place on October 6 at 15:49 UTC (+/-1 minute of uncertainty) while IS4OM prediction also showed that re-entry would occur on October 6 at 15:48:25 UTC. The corresponding impact point is in the North Atlantic Ocean,” ISRO informed.
The atmospheric re-entry of the rocket body within eight years of its launch is fully compliant with the international debris mitigation guidelines, in particular, the guideline of Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) that recommends limiting the post-mission orbital life of a defunct object in Low-Earth orbit (LEO) to 25 years.













