‘Worsening spread’ of deadly fungal infection raising alarm in U.S.
Global News
'Worrisome' CDC data was released amid an outbreak of the drug-resistant fungal infection, Candida auris, in U.S. long-term care facilities.
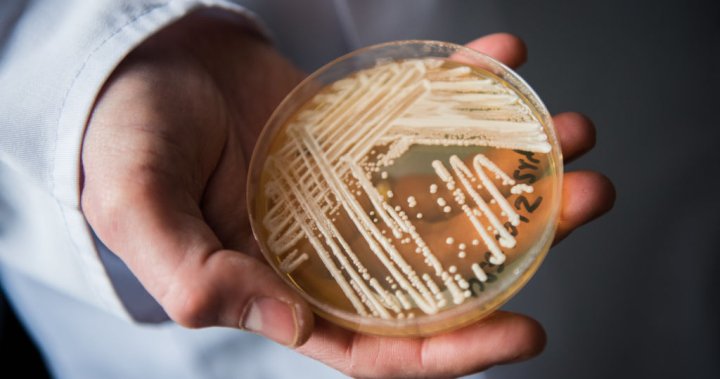
Cases of a drug-resistant infection caused by the fungus Candida auris are on the rise in the United States, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The fungal infection has proved deadly, especially for those with compromised immune systems, and has demonstrated an ability to spread easily in health-care settings.
The CDC data was published Monday in the Annals of Internal Medicine, amid an outbreak of fungal infections in long-term care facilities in Mississippi. The U.S. health agency found that cases of C. auris increased 95 per cent from 2020 to 2021 following a 44 per cent increase the year prior.
Preliminary figures estimate that there were 2,377 active C. auris infections across the U.S. in 2022, with 5,754 “colonization” cases. A colonization case denotes when a person has evidence of the fungus in their body without signs of an active infection.
C. auris, a type of yeast that can infect the bloodstream, is resistant to multiple anti-fungal drugs and is estimated to kill about 40 per cent of people who become infected, according to Health Canada. Even when patients survive, they can remain “colonized” with the fungus for years after treatment, the CDC says, and potentially pass it along unsuspectingly.
These fungal infections are of most concern to people who have been hospitalized for long periods of time, are at high risk of infection, or have medical implants. The organism often causes no symptoms in healthy people.
C. auris was first detected in the U.S. in 2016, though case numbers remained low until the “dramatic increase in 2021,” the CDC report reads. The fungus was first discovered in 2009 in Japan and has since caused outbreaks in numerous countries around the world.
Rising cases of C. auris infections, “especially in the most recent years, are really concerning to us,” said the study’s lead author, Dr. Meghan Lyman, chief medical officer in the CDC’s Mycotic Diseases Branch. “We’ve seen increases not just in areas of ongoing transmission, but also in new areas.”
“There’s still a lot to learn about colonization patterns,” Lyman said. “While (medicine) may treat the infection, we don’t have evidence that it completely eliminates C. auris from their body.”
