Untreatable gonorrhea may be on the horizon in Canada. Here’s why
Global News
As gonorrhea rates continue to climb in Canada, health officials are warning the infection is also developing more resistance to antibiotics.
As gonorrhea rates continue to climb in Canada, health officials are warning the infection is also becoming more resistant to antibiotics, which could lead to the possibility of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) becoming untreatable.
The World Health Organization (WHO) said in a media release on Monday that several countries, including Canada, are witnessing a growing number of treatment failures for gonorrhea.
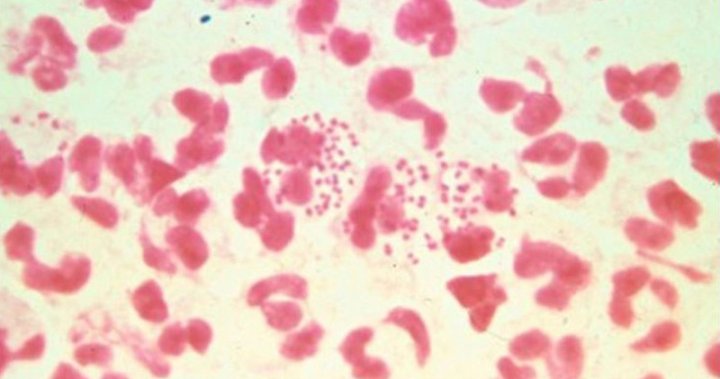
Gonorrhea, a common STI, is easily treated with modern drugs, such as ceftriaxone. However, a particular strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacteria responsible for causing gonorrhea, has developed a significant level of resistance to ceftriaxone and other antibiotics, like penicillin.
“Gonorrhea rates in Canada and globally have been increasing for many years,” said Dr. Ameeta Singh, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Alberta. “And every antibiotic that has been used to treat gonorrhea, it has developed resistance to rendering the antibiotic ineffective within a few years of starting to use it.”
Antimicrobial resistance in gonorrhea remains an important public health concern in Canada, according to the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC).
“Overall rates of gonococcal infection are increasing in Canada and it is more prevalent among adolescents and young adults,” a PHAC spokesperson told Global News in an email Tuesday. “Its’ causative agent, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, has acquired resistance or displayed decreased susceptibility to many antibiotics, leading to the possible emergence of untreatable gonorrhea in Canada.”
The symptoms of gonorrhea vary, but many with the infection, especially females, may have no symptoms at all, according to PHAC.
Symptoms in men may include a burning sensation when urinating, yellowish and/or white discharge from the penis, burning or itching at the opening of the penis and painful or swollen testicles.











