New non-invasive tool detects early stages of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
CTV
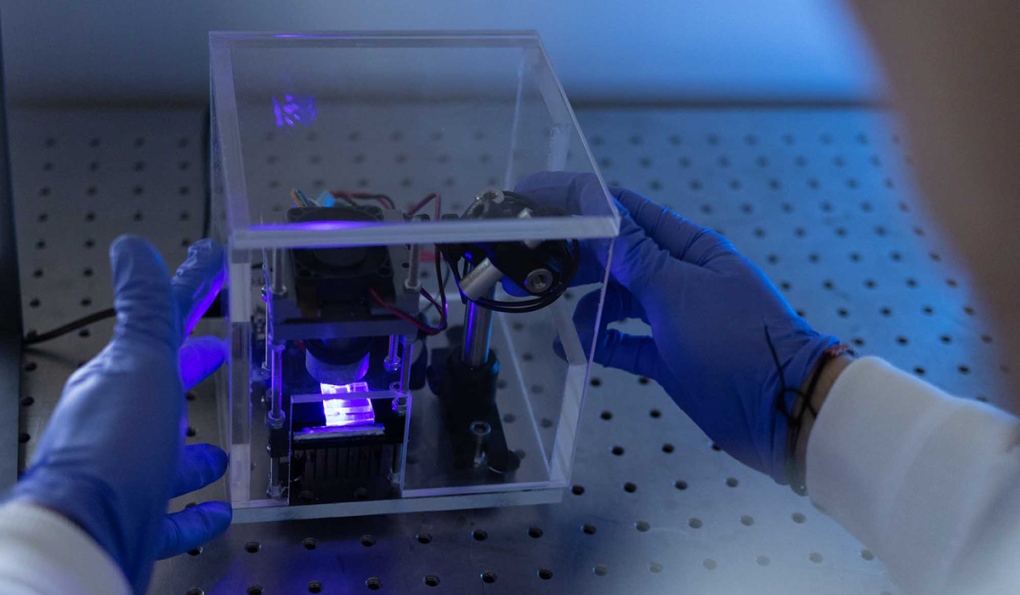
Researchers at Carleton University's Department of Electronics in Ottawa created a ground-breaking testing device to detect early signs of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s through biomolecular activities in a person’s saliva.
After a year-long wait for a neurologist in Halifax, Tracy Brander’s husband was diagnosed with young-onset Parkinson’s disease. Her husband, now 54, was 39 at the time.
“It wasn't bad for the first years, you know. But the past three years it has been terrible for him. He can hardly walk. He's in a lot of pain,” Brander told CTVNews.ca on Wednesday.
While the average age to develop Parkinson’s is around 60, young-onset occurs in five to 10 per cent of people diagnosed under 40, according to Parkinson Canada’s website.
Brander said she would like to know if any of her four children will get the disease, too, and with a personal family history of Alzheimer’s–another neurodegenerative disease–the Dalhousie University nursing student is looking for ways to get them diagnosed before showing any symptoms.
It's something that wouldn't have been possible decades ago, but new research means it is now an option for Brander's family.
Researchers at Carleton University's Department of Electronics in Ottawa created a ground-breaking testing device to detect early signs of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s through biomolecular activities in a person’s saliva.
The palm-sized, 3D-printed device has bio-electronic sensors helping monitor hormone concentration – such as dopamine, cortisol and a few other stress hormones – and protein aggregation for neurodegenerative diseases.




















 Run 3 Space | Play Space Running Game
Run 3 Space | Play Space Running Game Traffic Jam 3D | Online Racing Game
Traffic Jam 3D | Online Racing Game Duck Hunt | Play Old Classic Game
Duck Hunt | Play Old Classic Game